Dans le domaine des vaccins à ARNm et des thérapies à base d'acides nucléiques, les nanoparticules lipidiques (LNP) constituent les vecteurs essentiels pour une administration efficace des acides nucléiques. Les matériaux lipidiques sont des déterminants clés de l'efficacité et de la biosécurité de la délivrance par les LNP. Cependant, l'instabilité intrinsèque de l'ARNm a longtemps imposé le stockage des formulations de LNP à basse température. Les cristaux de glace et les contraintes osmotiques générés lors des cycles de congélation-décongélation peuvent facilement entraîner l'agrégation des LNP et la fuite d'ARNm, limitant considérablement leur application pratique.
Une équipe de l'Institut de chimie de l'Académie chinoise des sciences a publié dans Nature Communications une étude proposant une solution novatrice : exploiter le phénomène de cryoconcentration pour incorporer activement des cryoprotecteurs à base de bétaïne (CPA) dans des nanoparticules lipidiques (LNP). Cette approche permet non seulement de maintenir la stabilité de la formulation, mais aussi d'améliorer significativement l'efficacité de la délivrance d'ARNm. Cette étude ouvre de nouvelles perspectives pour l'optimisation des formulations lipidiques.

Contexte de la recherche
L'ARNm est extrêmement sensible à l'hydrolyse, à l'oxydation et à la dégradation enzymatique, ce qui nécessite une conservation à des températures inférieures à zéro pour assurer sa stabilité. Les vaccins à ARNm utilisés en clinique, tels que l'ARNm-1273 et le BNT162b2, utilisent le saccharose comme cryoprotecteur. Cependant, même avec des cryoprotecteurs, deux problèmes majeurs persistent lors des cycles de congélation-décongélation :
-
Perturbation de la stabilité physique : La formation de cristaux de glace et les changements de pression osmotique peuvent provoquer la fusion et l'agrégation des LNP, compromettant leur structure sphérique et l'uniformité de leur taille.
-
Efficacité de délivrance réduite : les dommages structurels aux LNP peuvent entraîner une fuite d’ARNm et un affaiblissement de l’échappement endosomal, réduisant finalement l’efficacité d’expression de l’ARNm dans les cellules cibles.
Alors que les recherches existantes se concentrent principalement sur la « stabilisation passive » des LNP, cette étude utilise de manière novatrice le processus de congélation-décongélation lui-même pour transformer les cryoprotecteurs de simples « stabilisateurs » en « activateurs fonctionnels », obtenant ainsi une double amélioration de la stabilité et de l'efficacité de la délivrance.
La concentration des données favorise l'intégration de BT-CPA dans les LNP
L'équipe de recherche a mis au point un cryoprotecteur composite (BT-CPA) composé de bétaïne et de tréhalose. Grâce à une série d'expériences, elle a démontré que la congélation induit l'incorporation active du BT-CPA dans les LNP, ce qui produit deux effets clés : (1) le maintien de l'intégrité structurale des LNP après des cycles de congélation-décongélation et (2) l'amélioration de la capacité des LNP à échapper aux endosomes, augmentant ainsi l'efficacité de la délivrance d'ARNm.
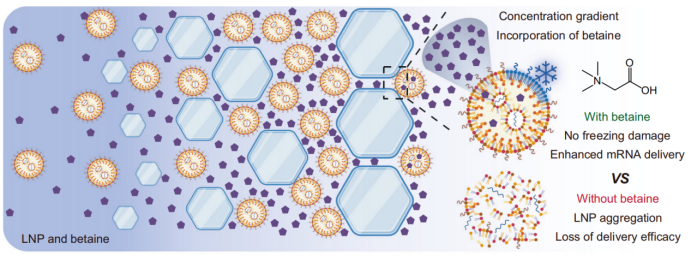
Lors de la congélation, l'eau forme des cristaux de glace, ce qui entraîne une forte augmentation des concentrations de LNP et de cryoprotecteurs dans la phase liquide restante — un phénomène appelé « concentration par congélation ». Ce processus crée un gradient de concentration important à travers la membrane des LNP, favorisant la diffusion passive de la bétaïne et du tréhalose à l'intérieur des LNP à travers des brèches transitoires dans la membrane lipidique (induites par les contraintes mécaniques des cristaux de glace et les transitions de phase lipidiques).
Les chercheurs ont validé ce mécanisme par résonance magnétique nucléaire du proton (RMN ¹H) et spectrométrie de masse à haute résolution : dans les échantillons LNP+BT-CPA soumis à des cycles de congélation-décongélation, les signaux caractéristiques de la bétaïne (pics à 3,28 ppm et 3,83 ppm) et du tréhalose (par exemple, pic à 3,34 ppm) étaient détectables même après dialyse pour éliminer le BT-CPA libre externe. En revanche, les échantillons LNP+BT-CPA non soumis à des cycles de congélation-décongélation présentaient une encapsulation minimale de BT-CPA. Ceci confirme que la congélation est nécessaire à l’incorporation du BT-CPA dans les LNP, au-delà d’une simple adsorption de surface.
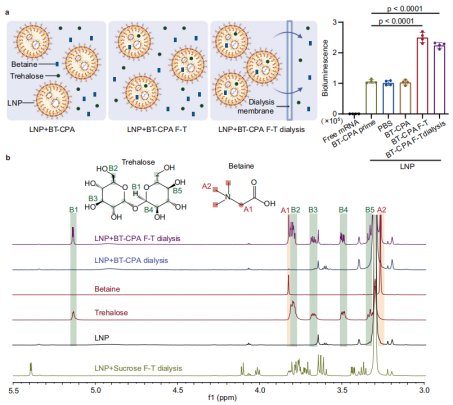
Optimisation du BT-CPA : contrôle précis de la concentration et du ratio
Afin d'équilibrer stabilité et efficacité de délivrance, les chercheurs ont systématiquement optimisé la concentration et le ratio de BT-CPA :
-
Optimisation du ratio de composition : L’utilisation de 25 mg/mL de bétaïne seule a permis de maintenir la stabilité des LNP, mais l’efficacité d’encapsulation de l’ARNm était légèrement inférieure à celle obtenue avec 87 mg/mL de saccharose. L’ajout de 25 mg/mL de tréhalose (BT-CPA : 25 mg/mL de bétaïne + 25 mg/mL de tréhalose) a entraîné des variations minimales de la taille des LNP après congélation-décongélation, une efficacité d’encapsulation de l’ARNm stable et une augmentation de l’efficacité de délivrance de 1,4 fois par rapport à la bétaïne seule, et de 2,4 fois par rapport aux LNP fraîches.
-
Effet de seuil de concentration : L'augmentation de la concentration de bétaïne de 10 mg/mL à 25 mg/mL a considérablement amélioré l'efficacité de la délivrance d'ARNm, mais des augmentations supplémentaires à 75 mg/mL n'ont apporté aucun gain supplémentaire, établissant ainsi 25 mg/mL comme la concentration optimale.
-
Optimisation du cycle de congélation-décongélation : 1 à 2 cycles ont amélioré l’efficacité de la délivrance sans endommager la structure des LNP, tandis que 6 cycles ont provoqué l’agrégation des LNP, une fuite d’ARNm et une efficacité réduite, identifiant 2 cycles comme optimaux.
BT-CPA améliore la délivrance d'ARNm en stimulant l'échappement endosomal.
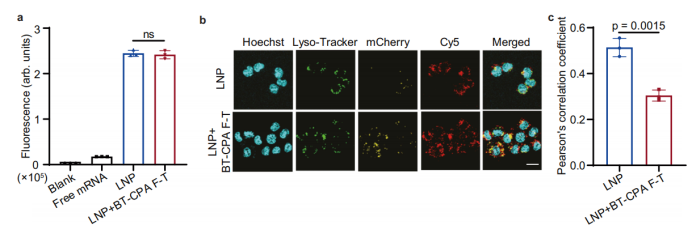
Grâce à des expériences cellulaires et à une validation mécanistique, les chercheurs ont démontré que le BT-CPA améliore l'efficacité de la délivrance non pas en affectant l'absorption cellulaire, mais en améliorant l'échappement endosomal pour stimuler l'expression de l'ARNm.
-
Absorption cellulaire inchangée, échappement endosomal accru : La cytométrie en flux a montré que l’efficacité d’absorption cellulaire des SM-102-LNP traitées au BT-CPA et soumises à des cycles de congélation-décongélation (BT-CPA-LNP) était quasiment identique à celle des SM-102-LNP non traitées. Cependant, la microscopie confocale a révélé un chevauchement significativement réduit entre l’ARNm marqué au Cy5 (rouge) et les marqueurs lysosomaux (vert) dans les BT-CPA-LNP, avec un coefficient de corrélation de Pearson (PCC) significativement plus faible que pour les LNP non traitées, indiquant un échappement endosomal accru.
-
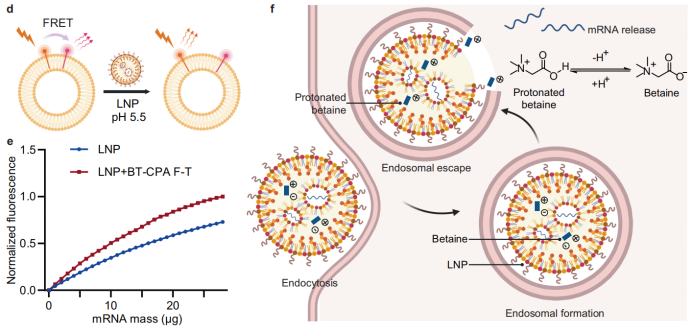
Mécanisme moléculaire : La protonation de la bétaïne induit la fusion membranaire : La bétaïne, une molécule zwitterionique, subit une protonation dans le milieu acide endosomal, acquérant une charge positive et favorisant les interactions électrostatiques avec les membranes endosomales chargées négativement, ce qui facilite la fusion. Des expériences de fusion membranaire réalisées avec des endosomes modèles marqués au NBD-PE et au Rhod-PE ont montré une déquenching de fluorescence NBD plus importante dans les BT-CPA-LNP, confirmant ainsi une capacité de fusion accrue.
-
Universalité : Compatibilité avec de multiples lipides : L’effet potentialisateur du BT-CPA ne se limite pas au SM-102, mais s’applique à divers lipides ionisables utilisés en clinique (par exemple, ALC-0315, MC3). Les LNP préparées avec ces lipides ont montré une efficacité de délivrance d’ARNm significativement améliorée après traitement au BT-CPA et cycles de congélation-décongélation, avec des tailles de particules inférieures à 200 nm et un PDI < 0,2, démontrant ainsi une large applicabilité.
Validation in vivo : une réponse immunitaire plus forte et un avantage en termes de réduction de la dose
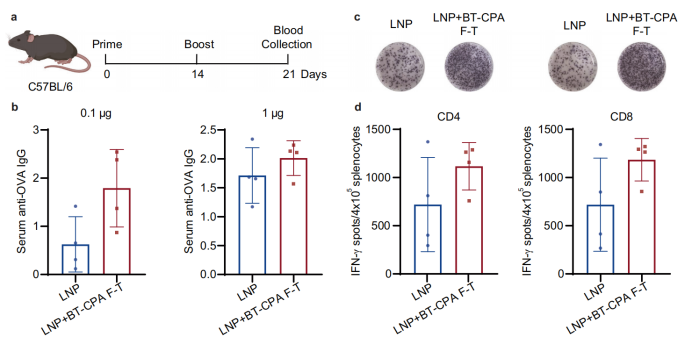
Chez les souris C57BL/6, les BT-CPA-LNP ont présenté des avantages significatifs :
-
Expression d'ARNm plus élevée : 4 h et 24 h après l'injection intramusculaire, l'expression de la luciférase dans les BT-CPA-LNP était respectivement 2,3 fois et 1,7 fois plus élevée que dans les LNP fraîches.
-
Réponse immunitaire plus forte : les BT-CPA-LNP encapsulant l'ARNm de l'ovalbumine (mOVA) ont induit des titres d'anticorps IgG spécifiques de l'OVA significativement plus élevés à des doses de 0,1 μg et 1 μg, et les tests ELISpot ont montré une augmentation des cellules T CD4⁺ et CD8⁺ positives à l'IFN-γ.
-
Excellente stabilité à long terme : après 6 mois à -80°C, les BT-CPA-LNP ont conservé une efficacité d'expression d'ARNm élevée avec une faible cytotoxicité (viabilité des cellules DC2.4 > 90 %).
Importance de la recherche
Cette étude propose non seulement une nouvelle stratégie de cryoprotection des LNP, mais redéfinit également les cryoprotecteurs comme des « composants actifs » pouvant s’incorporer aux LNP lors de la congélation afin d’en réguler la fonction. Principales contributions :
-
Optimisation des protocoles de stockage : relever les défis de stabilité liés au stockage et au transport à basse température des LNP, en soutenant la distribution mondiale des vaccins à ARNm et des médicaments à base d’acides nucléiques.
-
Développement des applications lipidiques : démonstration que des lipides comme le SM-102, l'ALC-0315 et le MC3 peuvent permettre une administration améliorée via le BT-CPA, aidant ainsi les applications en immunothérapie du cancer et en thérapie génique.
-
Conception de formulations innovantes : pionnier du concept « tirer parti de la congélation pour une amélioration fonctionnelle », offrant un nouveau paradigme pour le développement des LNP.
Conclusion
En utilisant stratégiquement le processus de congélation, cette recherche transforme les défis de stockage des LNP en avantages fonctionnels, fournissant une solution technique précieuse pour optimiser les formulations de lipides de base comme SM-102, ALC-0315 et MC3, avec des implications prometteuses pour le traitement des maladies.
SINOPEG fournit les lipides utilisés dans l'étude (SM-102, ALC-0315, MC3), proposant des excipients liposomaux clés en main ainsi qu'une gamme d'excipients lipidiques exclusifs. Nous fournissons également des polysaccharides et des produits polyzwitterioniques de haute qualité pour répondre à divers besoins en R&D et en production.
Référence
Cheng X, Zheng X, Tao K, et al. L'incorporation de bétaïne dans des nanoparticules lipidiques induite par la congélation améliore la délivrance d'ARNm. Nature Communications. 2025;16(1):4700.
À propos de nous
SINOPEG propose des solutions d'approvisionnement complètes et efficaces dans les domaines de l'administration de médicaments, des produits biopharmaceutiques et des sciences des matériaux.
Plateformes technologiques et produits de base :
-
Dérivés PEG pharmaceutiques/médicaux : PEG linéaires et structurés (multibras, en forme de V, en forme de Y, etc.).
-
Modificateurs de chaînes latérales d'acides gras : chaînes latérales de sémaglutide, de liraglutide et de tirzépatide, et liaisons peptidiques.
-
Plateforme lipidique (LNP) : Lipides LNP complets pour vaccins à ARNm, y compris des lipides cationiques exclusifs.
-
Plateforme de liaison ADC/ProTAC : Liaisons standard et personnalisées.
-
Plateforme de copolymères séquencés : vecteurs de médicaments à base de micelles macromoléculaires.
Certifiées ISO9001/13485/14001/45001, EcoVadis et GB/T29490, nos installations respectent les normes cGMP et les directives ICH-Q7A, garantissant des produits et services de haute qualité pour nos clients du monde entier.