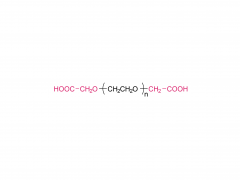
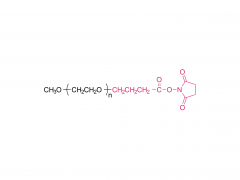
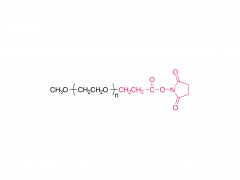
Le nom anglais complet est Bis-PEG21-NHS Ester
Poids moléculaire : environ 1 056 Da (la partie PEG pèse environ 924 Da)
Le nombre d'unités PEG est de 21
Groupe fonctionnel 1 N-hydroxysuccinimide (ester NHS)
Groupe fonctionnel 2 n-hydroxysuccinimide (NHS Ester)
Réactivité réagit avec les groupes amino primaires (-NH₂)
Il se présente sous la forme d'une poudre solide blanche à blanc cassé
Solubilité : Facilement soluble dans le DMSO et le DMF, et soluble dans l'eau (mais sujet à l'hydrolyse en solution aqueuse).
Conditions de conservation : À conserver à -20 °C dans un endroit sec et à l’abri de la lumière. Éviter toute déliquescence. Il est recommandé de remplir d’azote pour la protection.
⚙️ Fonctions principales et mécanismes d'action
Le BIS-PEG21-NHS ESTER est un agent de réticulation bifonctionnel homogène, mais sa structure PEG à longue chaîne lui confère des applications spécifiques. Sa fonction principale est :
Réaction avec le groupe amino primaire :
Les deux groupes esters NHS peuvent réagir efficacement avec le groupe amino primaire (-NH₂) sur les biomolécules pour former des liaisons amide stables.
Ces groupes amino primaires sont largement présents dans :
Protéine/Anticorps : Chaînes latérales de résidus de lysine.
Polypeptide : chaîne latérale amino ou lysine N-terminale.
Acides nucléiques avec modifications amino (tels que l'ADN/ARN amino-modifié).
Groupes aminés sur divers médicaments ou composés à petites molécules.
Introduisez les bras d'espacement PEG longs :
C'est sa fonction la plus cruciale. La chaîne PEG à 21 unités fournit une longue chaîne flexible d'environ 2,65 nanomètres de long.
Fonction 1 : Surmonter l'encombrement stérique. Lors de la connexion de deux macromolécules (telles que des anticorps et des enzymes), le PEG à longue chaîne peut surmonter efficacement la barrière spatiale qui les sépare et éviter toute interférence mutuelle due à une trop grande proximité des molécules.
Fonction 2 : Améliorer la solubilité et la flexibilité dans l'eau. La chaîne PEG améliore considérablement la solubilité dans l'eau de l'ensemble du produit de couplage et, grâce à sa flexibilité, augmente la liberté conformationnelle de la molécule, favorisant ainsi le maintien de l'activité biologique.
Fonction trois : réduire l’immunogénicité. Les chaînes PEG peuvent protéger certains épitopes antigéniques sur les conjugués et réduire l’immunogénicité.
L'application du BIS-PEG21-NHS ESTER est très spécifique et importante :
Réticulation protéine-protéine
Il est utilisé pour lier deux protéines différentes, par exemple pour lier des enzymes à des anticorps, pour préparer des réactifs de détection pour des immunoessais (tels que l'ELISA).
Synthèse de conjugués anticorps-médicament (ADC)
Dans la recherche et le développement d'ADC, il peut être utilisé pour lier des anticorps et des toxines à petites molécules contenant des groupes aminés. Ses bras PEG à longue chaîne contribuent à maintenir la solubilité de l'ADC et peuvent influencer ses propriétés pharmacocinétiques.
Modification de la peg-ylation
Bien que le réactif de peG-ylation typique soit le mPEG-NHS (fonction unique), le Bis-PEG-NHS peut être utilisé pour introduire des couches de PEG ramifiées ou en réseau à la surface de molécules telles que les protéines, ce qui peut obtenir de meilleurs effets de blindage et de stabilisation.
Construction de biocapteurs
Les molécules biométriques (telles que les anticorps, les aptamères) sont fixées à une extrémité sur la surface de l'électrode ou de la puce, tandis que l'autre extrémité est connectée à des molécules rapporteuses (telles que des enzymes, des colorants fluorescents) pour construire une interface de biodétection hautement sensible.
Fonctionnalisation des nanomatériaux
Modifier des nanoparticules (telles que des nanoparticules d’or et des points quantiques) et introduire simultanément deux molécules fonctionnelles différentes sur leurs surfaces pour obtenir une multifonctionnalisation.